刷题技巧总结
位掩码技巧
原理讲解
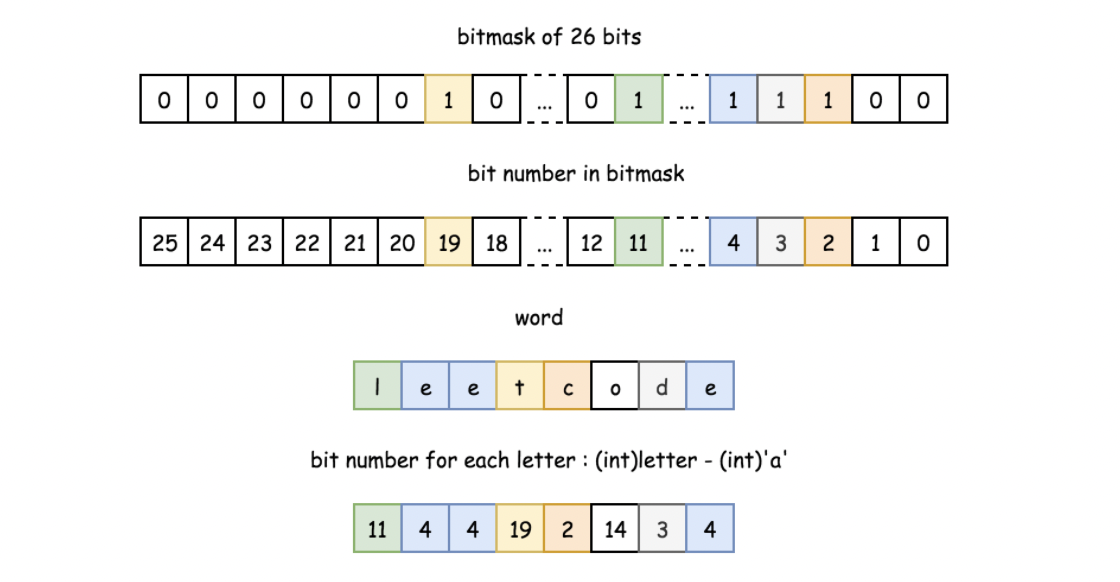
用于快速判断是否有重复出现的字符。限制条件为必须均为小写字母构成(不是必须),则可以使用位掩码技巧:用一个(长度为26比特位,1表示含有该字母,0表示不含有)数存储字符串包含字母情况,则判断两个字符串可以通过两个位掩码数与计算是否为0(num1 & num2 == 0 ?)。
如何设置掩码的第 n 位?使用标准的位操作:
n_th_bit = 1 << n。如何计算一个单词的位掩码?遍历单词的每个字母,计算该字母在掩码中的位置
n = (int)ch - (int)'a',然后创建一个第 n 位为 1 的掩码n_th_bit = 1 << n,通过或操作将该码合并到位掩码中bitmask |= n_th_bit。
LeetCode例题

代码如下:
func maxProduct(words []string) int {
// 双循环
// 判断两个单词是否有相同字母,用位掩码
result, n := 0, len(words)
bitsWords := make([]int, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
length := len(words[i])
temp := 0
for j := 0; j < length; j++ {
t := int(words[i][j] - 'a')
temp |= 1 << t
}
bitsWords[i] = temp
}
for i := 0; i < n - 1; i++ {
for j := i + 1; j < n; j++ {
if bitsWords[i] & bitsWords[j] == 0 {
result = max(result, len(words[i]) * len(words[j]))
}
}
}
return result
}
func max(x, y int) int {
if x > y {
return x
}
return y
}
回文串中心扩展技巧
计算有多少个回文子串的最朴素方法就是枚举出所有的回文子串,而枚举出所有的回文字串又有两种思路,分别是:
-
枚举出所有的子串,然后再判断这些子串是否是回文,复杂度为O(n^3)
-
枚举每一个可能的回文中心,然后用两个指针分别向左右两边拓展,当两个指针指向的元素相同的时候就拓展,否则停止拓展,复杂度可以降低到O(n^2)
注意考虑单个中心和两个中心的情况
func countSubstrings(s string) int {
// 中心扩展
n := len(s)
result := 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
result += getCount(s, n, i)
}
return result
}
func getCount(s string, n, index int) int {
count := 1
// 单中心
left, right := index-1, index+1
for left >= 0 && right < n {
if s[left] != s[right] {
break
}
count++
left--
right++
}
// 双中心
left, right = index, index+1
for left >= 0 && right < n {
if s[left] != s[right] {
break
}
count++
left--
right++
}
return count
}
前缀树(Trie)技巧
前缀树又叫字典树,英文名是Trie。就是一个像字典的树。用于快速查询「某个字符串/字符前缀」是否存在的数据结构。实现方面有两种方式:二维数组和TrieNode结构节点。

TrieNode结构节点实现代码:
type Trie struct {
// 26叉树实现
child [26]*Trie
}
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
func Constructor() Trie {
return Trie{}
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
func (this *Trie) Insert(word string) {
p := this
for i := 0; i < len(word); i++ {
if p.child[int(word[i]-'a')] == nil {
node := &Trie{}
p.child[int(word[i]-'a')] = node
}
p = p.child[int(word[i]-'a')]
}
}
注意:节点结构体除了包含子节点外,可以包含isEnd标志符标志是否是某个单词结尾,也可以设定count统计叶子节点数目,用于判断当前节点是否是叶子节点。
缺点
前缀树在算法上是很常见的一种数据结构,但有如下不足:
- 字符集大小不好确定,上述题目只考虑了26个小写字母。
- 个别超长字符会使Trie进一步变深,如果 Trie 是存储在硬盘中,Trie 结构过深带来的影响是多次随机 IO,随机 IO 是成本很高的操作。
- 同时 Trie 的特殊结构,也会为分布式存储将会带来困难。
二分查找中小技巧
计算mid时避免溢出
mid := left + (right-left)>>1mid = int(uint(left+right) >> 1)官方源代码sort.Search()方法中使用的。
2. Sort.Search()使用
func Search(n int, f func(int) bool) int函数采用二分搜索找到区间[0, n)内最小的满足f(i) == true的i值。
源代码如下:

最小堆、最大堆技巧
在用heap包实现最小堆、最大堆时,有一些额外的技巧。主要是一些函数的使用场景总结:
1. Init(h Interface)函数
该函数作用是初始化堆,复杂度为O(n)。
一般创建堆后,如果需要一个一个插入的场景,则使用Push()即可,但对于需要一次插入多个元素时,可以先一次性插入,在调用Init()函数即可。
如下面官方文档中的优先队列使用示例:

2. Fix(h Interface, i int)函数
在修改第i个元素后,调用本函数修复堆,比删除第i个元素后插入新元素更有效率。复杂度O(log(n)),其中n等于h.Len()。
3. Remove(h Interface, i int) interface{}函数
删除堆中的第i个元素,并保持堆的约束性。复杂度O(log(n)),其中n等于h.Len()。
注意:删除的第i个元素是排序后的第i个,所以可用于删除堆中第几小(大)的元素。
即Pop(h)等价于Remove(h, 0)。
KMP算法
如果是暴力匹配过程:每一次子串都需要回退到第一个字符,而被匹配的串要回退到开始匹配位置的下一个位置,重新开始匹配。
KMP算法是一种字符串匹配算法,可以在 O(n+m) 的时间复杂度内实现两个字符串的匹配。
next数组
next数组是对于模式串而言的。模式串P的next数组定义为:next[i] 表示 P[0] ~ P[i] 这一个子串,使得 前k个字符恰等于后k个字符 的最大的k。
注意:k不能取i+1,因为子串一共有i+1个字符,自己和自己相等,没有意义。
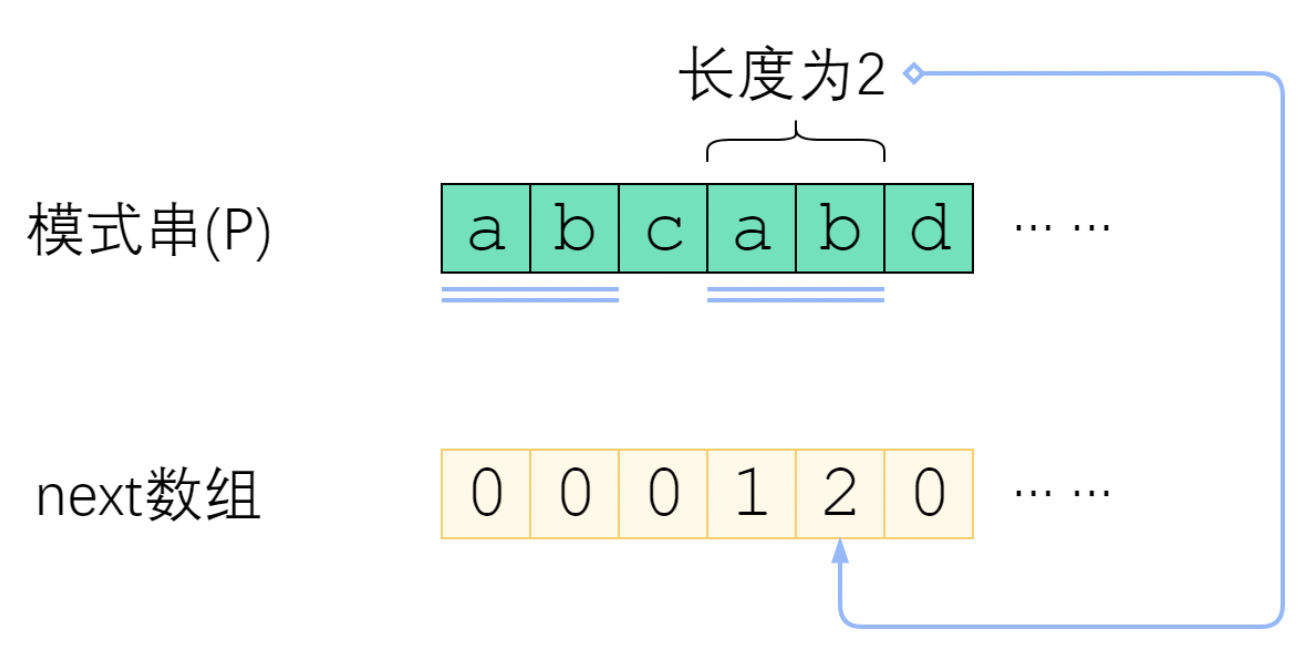
2. 快速构建next数组
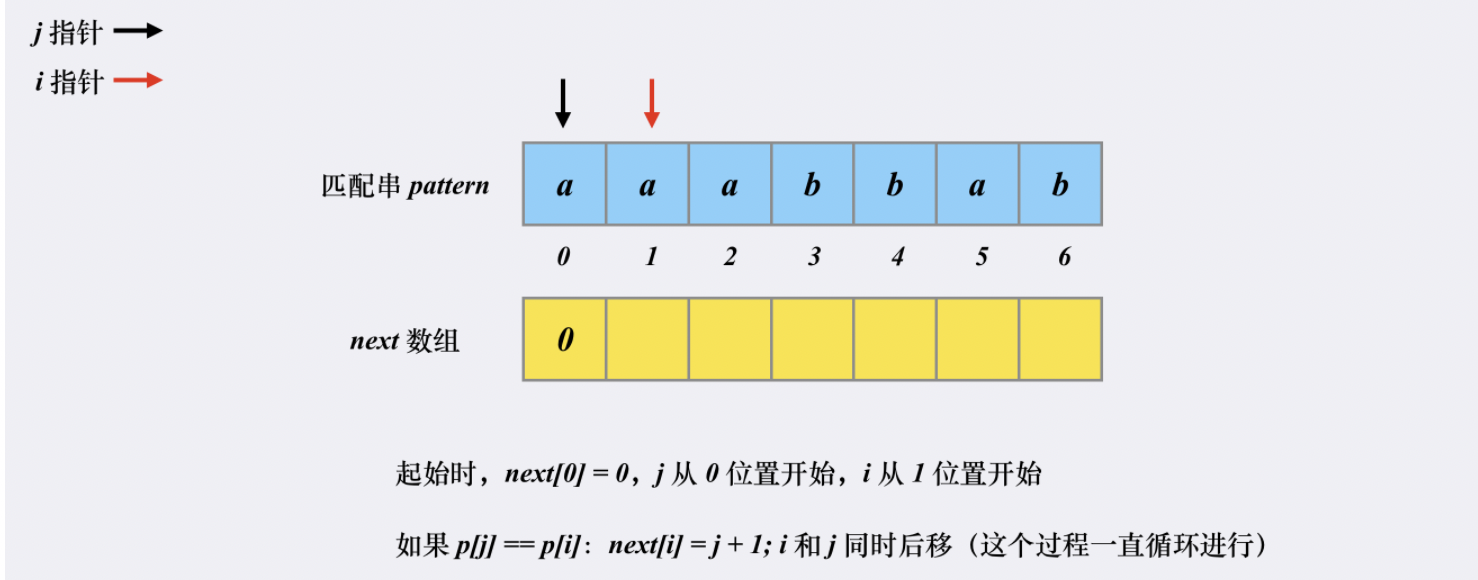
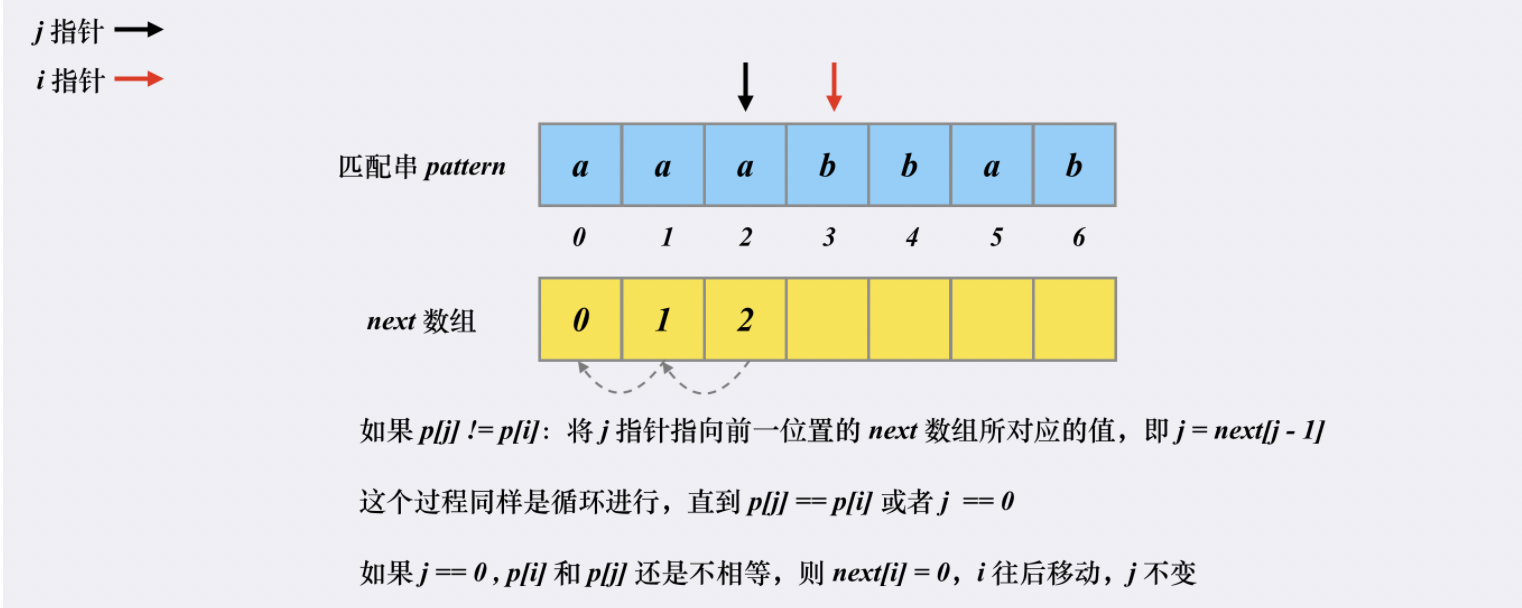
快速构建next数组也是匹配的过程:
calcMaxMatchLengths := func(s []byte) []int {
next := make([]int, len(s))
for i, c := 1, 0; i < len(s); i++ {
v := s[i]
for c > 0 && s[c] != v {
c = next[c-1]
}
if s[c] == v {
c++
}
next[i] = c
}
return next
}
使用next数组进行匹配
如果出现不匹配情况,则会检查之前已经匹配成功的部分中里是否存在相同的「前缀」和「后缀」。如果存在,则跳转到「前缀」的下一个位置继续往下匹配。

代码如下:
kmpSearch := func(text, pattern []byte) (pos []int) {
next := calcMaxMatchLengths(pattern)
lenP := len(pattern)
c := 0
for i, v := range text {
for c > 0 && pattern[c] != v {
c = next[c-1]
}
if pattern[c] == v {
c++
}
if c == lenP {
pos = append(pos, i-lenP+1)
c = next[c-1] // 不允许重叠时 c = 0
// 匹配是否存在时,直接返回true
}
}
return
}
4. LeetCode例题

代码如下
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func isSubtree(root *TreeNode, subRoot *TreeNode) bool {
// 先序遍历匹配
nullLeft, nullRight := math.MinInt32, math.MaxInt32
var dfs func(root *TreeNode, path *[]int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, path *[]int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
*path = append(*path, root.Val)
if root.Left != nil {
dfs(root.Left, path)
} else {
*path = append(*path, nullLeft)
}
if root.Right != nil {
dfs(root.Right, path)
} else {
*path = append(*path, nullRight)
}
}
if subRoot == nil {
return true
}
var pathRoot, pathSubRoot []int
dfs(root, &pathRoot)
dfs(subRoot, &pathSubRoot)
// KMP算法匹配子串
subLen := len(pathSubRoot)
// 1.构建next数组
next := make([]int, subLen)
for i, c := 1, 0; i < subLen; i++ {
v := pathSubRoot[i]
for c > 0 && pathSubRoot[c] != v {
c = next[c-1]
}
if pathSubRoot[c] == v {
c++
}
next[i] = c
}
// 2.匹配过程
c := 0
for _, v := range pathRoot {
for c > 0 && pathSubRoot[c] != v {
c = next[c-1]
}
if pathSubRoot[c] == v {
c++
}
if c == subLen {
return true
}
}
return false
}
 NarcissusBlog
NarcissusBlog